
Back مقابل غير ضوئي Arabic Dijastereoizomer BS Diastereòmer Catalan Diastereomer Czech Diastereomer German Diastereoisómero Spanish Diastereomeer Estonian Diastereoisomero Basque دیاستریومر Persian Diastereomeeri Finnish
This article needs additional citations for verification. (September 2021) |
| Diastereomers that are also epimers | |
|---|---|
|
|

|

|
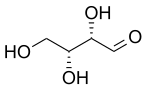
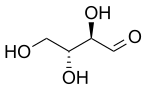
| D-threose | D-erythrose |
In stereochemistry, diastereomers (sometimes called diastereoisomers) are a type of stereoisomer.[1] Diastereomers are defined as non-mirror image, non-identical stereoisomers. Hence, they occur when two or more stereoisomers of a compound have different configurations at one or more (but not all) of the equivalent (related) stereocenters and are not mirror images of each other.[2] When two diastereoisomers differ from each other at only one stereocenter, they are epimers. Each stereocenter gives rise to two different configurations and thus typically increases the number of stereoisomers by a factor of two.
Diastereomers differ from enantiomers in that the latter are pairs of stereoisomers that differ in all stereocenters and are therefore mirror images of one another.[3] Enantiomers of a compound with more than one stereocenter are also diastereomers of the other stereoisomers of that compound that are not their mirror image (that is, excluding the opposing enantiomer). Diastereomers have different physical properties (unlike most aspects of enantiomers) and often different chemical reactivity.
Diastereomers differ not only in physical properties but also in chemical reactivity — how a compound reacts with others. Glucose and galactose, for instance, are diastereomers. Even though they share the same molar weight, glucose is more stable than galactose. This difference in stability causes galactose to be absorbed slightly faster than glucose in human body.[4][5]
Diastereoselectivity is the preference for the formation of one or more than one diastereomer over the other in an organic reaction. In general, stereoselectivity is attributed to torsional and steric interactions in the stereocenter resulting from electrophiles approaching the stereocenter in reaction.[6]
- ^ IUPAC "Gold Book" diastereoisomerism doi:10.1351/goldbook.D01679
- ^ Garrett, R.H.; Grisham, C.M. (2005), Biochemistry 3rd ed., Belmont CA: Thomson, p. 205, ISBN 0-534-41020-0.
- ^ IUPAC "Gold Book" enantiomer doi:10.1351/goldbook.E02069
- ^ McCance, Robert Alexander; Madders, Kate (1930). "The comparative rates of absorption of sugars from the human intestine". Biochemical Journal. 24 (3): 795–804. doi:10.1042/bj0240795. ISSN 0264-6021. PMC 1254520. PMID 16744419.
- ^ Chao, Hsi-Chun; McLuckey, Scott A. (2020-10-06). "Differentiation and Quantification of Diastereomeric Pairs of Glycosphingolipids using Gas-phase Ion Chemistry". Analytical Chemistry. 92 (19): 13387–13395. doi:10.1021/acs.analchem.0c02755. ISSN 0003-2700. PMC 7544660. PMID 32883073.
- ^ Lavinda, Olga; Witt, Collin H.; Woerpel, K. A. (2022-03-28). "Origin of High Diastereoselectivity in Reactions of Seven-Membered-Ring Enolates". Angewandte Chemie International Edition in English. 61 (14): e202114183. doi:10.1002/anie.202114183. ISSN 1521-3773. PMC 8940697. PMID 35076978.