
Back Synucleinopathie German سینوکلئینوپاتی Persian Synucléinopathie French シヌクレイノパチー Japanese Sinukleinopatija Serbian
| Synucleinopathy | |
|---|---|
| Other names | α-Synucleinopathies |
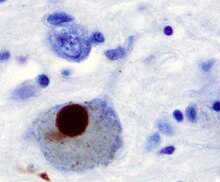 | |
| Positive α-Synuclein staining of a Lewy body in a patient with Parkinson's disease. | |
| Specialty | Neurology |
Synucleinopathies (also called α-Synucleinopathies) are neurodegenerative diseases characterised by the abnormal accumulation of aggregates of alpha-synuclein protein in neurons, nerve fibres or glial cells.[1] There are three main types of synucleinopathy: Parkinson's disease (PD), dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB), and multiple system atrophy (MSA).[1] Other rare disorders, such as various neuroaxonal dystrophies, also have α-synuclein pathologies.[2] Additionally, autopsy studies have shown that around 6% of sporadic Alzheimer's Disease exhibit α-synuclein positive Lewy pathology, and are sub-classed as Alzheimer's Disease with Amygdalar Restricted Lewy Bodies (AD/ALB).[3][4][5][6][7]
- ^ a b McCann H, Stevens CH, Cartwright H, Halliday GM (2014). "Α-Synucleinopathy phenotypes". Parkinsonism & Related Disorders. 20 (Suppl 1): S62–S67. doi:10.1016/S1353-8020(13)70017-8. hdl:1959.4/53593. PMID 24262191.
- ^ Goedert M, Jakes R, Spillantini MG (2017). "The Synucleinopathies: Twenty Years On". J Parkinsons Dis. 7 (s1): S53–S71. doi:10.3233/JPD-179005. PMC 5345650. PMID 28282814.
- ^ Arai, Yasushi; Yamazaki, Mineo; Mori, Osamu; Muramatsu, Hiromi; Asano, Goro; Katayama, Yasuo (January 2001). "α-Synuclein-positive structures in cases with sporadic Alzheimer's disease: morphology and its relationship to tau aggregation". Brain Research. 888 (2): 287–296. doi:10.1016/S0006-8993(00)03082-1. PMID 11150486. S2CID 3044534.
- ^ Nelson, Peter T; Abner, Erin L; Patel, Ela; Anderson, Sonya; Wilcock, Donna M; Kryscio, Richard J; Van Eldik, Linda J; Jicha, Gregory A; Gal, Zsombor; Nelson, Ruth S; Nelson, Bela G; Gal, Jozsef; Azam, Md. Tofial; Fardo, David W; Cykowski, Matthew D (1 January 2018). "The Amygdala as a Locus of Pathologic Misfolding in Neurodegenerative Diseases". Journal of Neuropathology & Experimental Neurology. 77 (1): 2–20. doi:10.1093/jnen/nlx099. PMC 5901077. PMID 29186501.
- ^ Hamilton, Ronald L. (5 April 2006). "Lewy Bodies in Alzheimer's Disease: A Neuropathological Review of 145 Cases Using α-Synuclein Immunohistochemistry". Brain Pathology. 10 (3): 378–384. doi:10.1111/j.1750-3639.2000.tb00269.x. PMC 8098522. PMID 10885656.
- ^ Toledo, Jon B.; Gopal, Pallavi; Raible, Kevin; Irwin, David J.; Brettschneider, Johannes; Sedor, Samantha; Waits, Kayla; Boluda, Susana; Grossman, Murray; Van Deerlin, Vivianna M.; Lee, Edward B.; Arnold, Steven E.; Duda, John E.; Hurtig, Howard; Lee, Virginia M.-Y.; Adler, Charles H.; Beach, Thomas G.; Trojanowski, John Q. (March 2016). "Pathological α-synuclein distribution in subjects with coincident Alzheimer's and Lewy body pathology". Acta Neuropathologica. 131 (3): 393–409. doi:10.1007/s00401-015-1526-9. PMC 4754135. PMID 26721587.
- ^ Uchikado, Hirotake; Lin, Wen-Lang; DeLucia, Michael W.; Dickson, Dennis W. (July 2006). "Alzheimer Disease With Amygdala Lewy Bodies: A Distinct Form of α-Synucleinopathy". Journal of Neuropathology and Experimental Neurology. 65 (7): 685–697. doi:10.1097/01.jnen.0000225908.90052.07. PMC 5706655. PMID 16825955.